
Artificial technologies are changing the world at a rapid speed. For instance, Artificial Intelligence Agents also known as AI Agents are at the table for the service.
The heat of this transcending technology is imperative and fortune 500 companies are using AI Agents for variety of tasks and by the most, developing custom AI Agents for domain-specific tasks.
AI Agents have its own brain that could think, plan, action, and learn to improve its efficiency. For example, you can ask AI Agent to book a flight from your source to destination at a given date and time with budget allocation.
And bam! These agents are highly intelligence to understand user query, thanks to LLM at its core that perform multiple processes to accomplish the objective.
Today, the application of Agentic AI emerged as an essence. Be it marketing, sales, development, finance, healthcare and more. These autonomous agents are well-versed to tackle field of jobs with speed and accuracy.
In this blog, we will learn about what AI Agent do and its core components along with their types and methods to develop an AI Agents.
What Is AI Agent?
In general term, AI Agents are software system that perceive information, understand context, reason steps, and execute action on their own to achieve the end objective.
In technology terms, AI Agents are powered by multimodal large language models (LLMs), trained on massive deep learning architectures, that demonstrate emergent abilities enabling them to plan and perform tasks autonomously.
In data science language, AI Agents are computational entity that can perceive its environment via data inputs, decide and reason using machine learning, act considering trained algorithms to produce output and learn by improving performance over time.
An effective prompt play an important role because it guide agents with context and information it may require for effective task completion.
Let’s understand its core components.
What Are The Components Of AI Agents?
Unlike chatbots, AI Agents can PLAN, DECIDE, ACT, and LEARN through its components assistance:
- Instruction (prompt)
- Planning Engine (LLM)
- Memory (Databases)
- Tools (External apps)
- Feedback (Iteration process)
1. Instructions
Instructions act as a fuel for AI Agents which is given by a user. Unlike standard prompting, AI Agents demand structured prompts to reason, plan, and act.
Thus, prompts that include structured instructions help Agents understand the task clearly and effectively. Every prompt have some goals to be finished. Therefore, AI Agents are intelligent enough to understand your prompt and end objectives.
Speaking of prompt, it could be both long and short based on the context, reasoning, and instructions you need to give the model. On average, the structured prompt length is 500-2000 tokens including role, memory, rules, constraints, and examples.
However, for severe use cases like legal document review, a context prompt length would require 2,000-10,000 tokens because of the long contract content.
For Example., A legal contract review agent that review every aspect of legal contract and cases. Now, Imagine you inject full contract into the prompt (20–40 pages of contract text) and add instructions “Highlight risky clauses, compare with standard terms, and suggest revisions.”
2. Planning Engine
Planning engine is the brain of the AI Agent which utilizes high-stack LLM to reason user’s prompt and puts into an effective action to achieve the objective without fail.
Think of it in this manner, the planning engine is the reasoning module inside an AI Agent that takes a goal or instruction from the user, decomposes into small, actionable steps. Immediately decides the order of execution and monitors progress until the goal is achieved.
It is the main component of AI Agent which distinct it from normal chatbot, engage in multi-step, open-ended tasks.
For Example., “Research the top 5 competitors in renewable energy, compare their financials, and create a report with charts.”
Here, the planning engine would break it into categories as required. Search competitors, fetch financial data, analyse number, generate charts, and write structured report.
3. Memory
Memory is essential for AI Agent or agentic tasks. It basically store, retrieve, and reuse past information (context, data, or interactions) so the agent can look into past conversation or learn from previous mistakes.
If enable, AI Agents can provide personalized response including maintaining long-form context. These required high-efficient memory processing capabilities to fetch past data.
There are two critical memory types classification of AI Agent:
i) Short-Term Memory
It is also known as conversational memory that keeps track of the current session or conversation. For example,
- User: “Book me a flight to Paris.”
- Later: “Make it business class.”
- The agent remembers “Paris flight” from the same session.
ii) Long-Term Memory
Persists across sessions, days, or months. For effective results, it being stored in a database or vector store. For example,
- Previously: “Always book morning flights with Delta.”
- Even if you come back a week later, the agent recalls that.
OpenAI’s AI Agent software uses both memory management to provide efficient and effective response.
4. Tools
Tools are like superpowers for AI Agents. It is because it gives special ability to the agent to complete tasks. Tools may refers to external APIs, functions, and modules.
Unlike LLM and Memory, Tools are external entity that LLM connects with it to make the required task done because tools give agents actionability, accuracy, and real-world integration.
There are various types of Tools In AI Agents:
i) Knowledge & Retrieval Tools: Fetch external knowledge beyond model’s training cutoff. For example, SERPAPI and Vector Databases for respective task execution.
ii) Computation Tools: They are technical tools used for accurate math, data analysis, or logic. For example, Python/NumPy execution environments or Wolfram Alpha API.
iii) Communication Tools: Allow agents to send/receive messages, emails, or notifications. For example, Gmail or Outlook API and Slack, Discord, WhatsApp integrations.
iv) Multimodal Tools: Multimodal tools are trained multimodal LLMs that understand beyond text, meaning trained to understand combined data types like audio, video, and speech. For example, RunwayML and Pika Labs.
5. Feedback
Feedback is the process of evaluating the agent’s own actions or outputs (sometimes with human help, sometimes autonomously), and then using that evaluation to adjust future behavior. Most of modern AI Agents facilitate self-correction feedback mechanism, minimizing human intervention.
And it is important from the prospective of reducing hallucinations and improves decision-making over time. This way AI Agent system build trust and provide optimum result for real-world use.
What Are The Types Of AI Agents?
The classification of AI Agent is divided into six types based on their response and intelligence expectation.
1. Simple Reflex Agent
This is the most basic and simple type of Agent in AI. It action operate on the ‘If then, then that’ function. Such type of agent act straight-forward toward a task.
While it can take action based on the current situation, it cannot think and plan because it doesn’t have any brain and memory.
For Example., If an agent see someone on the door, it open the door for them automatically.
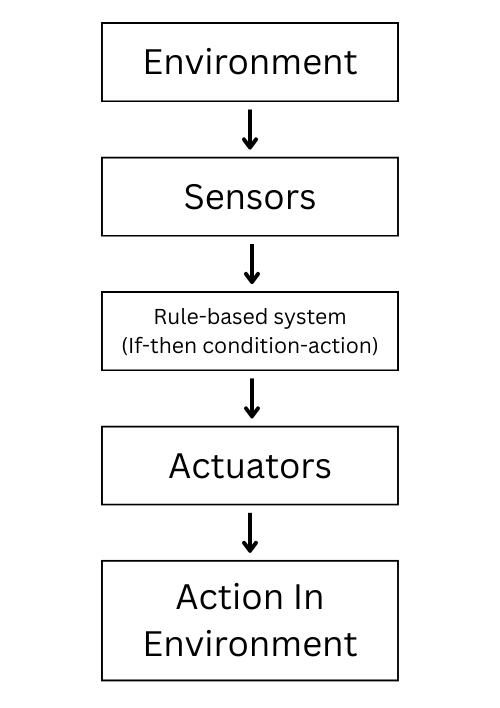
Use cases of simple reflex AI Agents
- Motion-activated lighting which turn on and off learning occupancy by sensors.
- Thermostats that detect real-world atmosphere to switch heating off/cooling on.
- Traditional assembly line machine which stops operation in full if fault detection is observed.
2. Model Reflex Agent
Model reflex agent have internal memory in its architecture which makes it better than simple reflex model. The internal model has memory that act as a database to store and retrieve information in a state manner.
It can handle situation where the current input is not enough. Also, determine from past interaction or previous state to provide better action for a particular task.
For Example., If you said agent to call you Aarohi… from the next moment, it remember your name and interact with you referring your name.
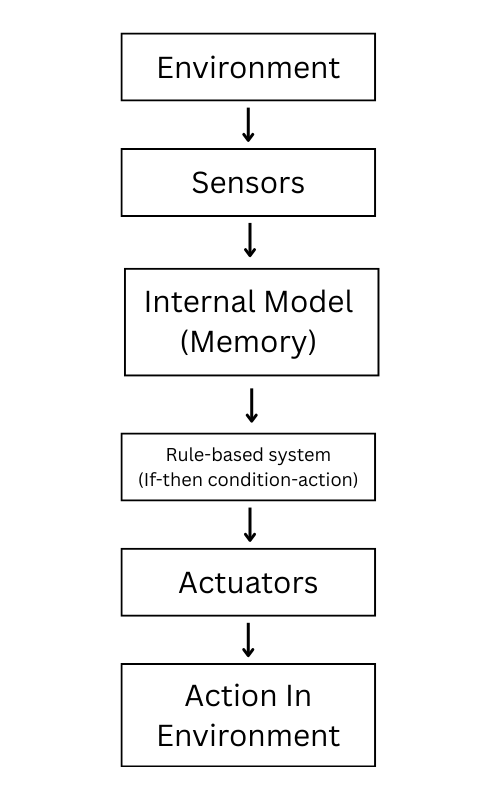
Use cases of model reflex AI Agent
- Giving command to Alexa to play song or a particular task process information using reflex model.
- Examine deviations in production comparing real-time data to control product quality.
- Ring doorbell cameras recognizes people vs packages to decides whether to alert.
3. Goal-Based Agent
Goal-based agent are smarter because they can think, plan, and react intelligently to achieve the end objective or task or goal. While they think before reacting, these agents can planning necessary structure to complete the goal.
On top of that, these agents can reconstruct structure if the previous state of action fails to complete the goal. Hence, making it flexible for a goal oriented tasks.
They explicitly ask questions like ‘what to do to solve the situation?’ or ‘what to do to get closer to the goal?’
For Example., GPS system that guides you the best route to reach the destination.
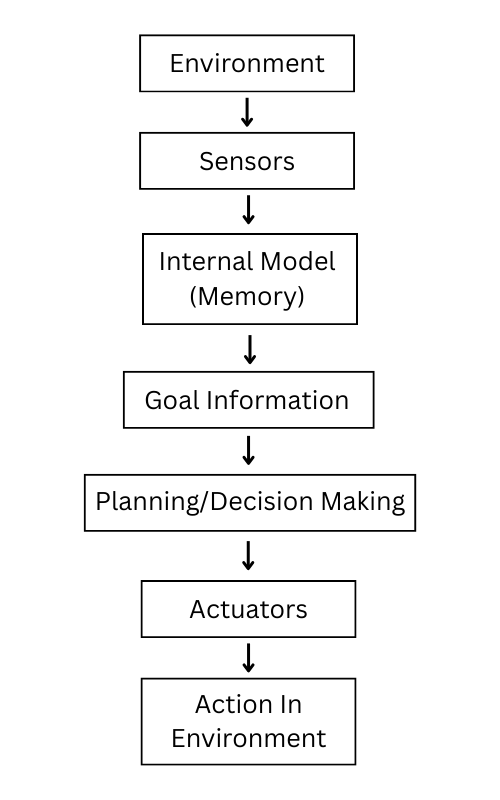
Use cases of goal-based AI Agent
- Autonomous robots in industries to decide how to navigate products in dynamic environment.
- Map-based applications that calculates routes to help user to reach to the destination.
- Evaluate inventory levels and inform respective departments with necessary information.
4. Utility-Based Agent
The utility agent is also a goal-based agent but with a smart optimization technique. These agent aims to improve decision making through a quantitative measure (utility score) where each attribute have a number and highest number represent a greater preference.
Utility score is calculated using the mathematical expression. These agents develop utility score towards each possible performance and pick the one with the highest score.
For Example., An AI agent playing chess and figuring out best move using utility score to finish the playing quickly.
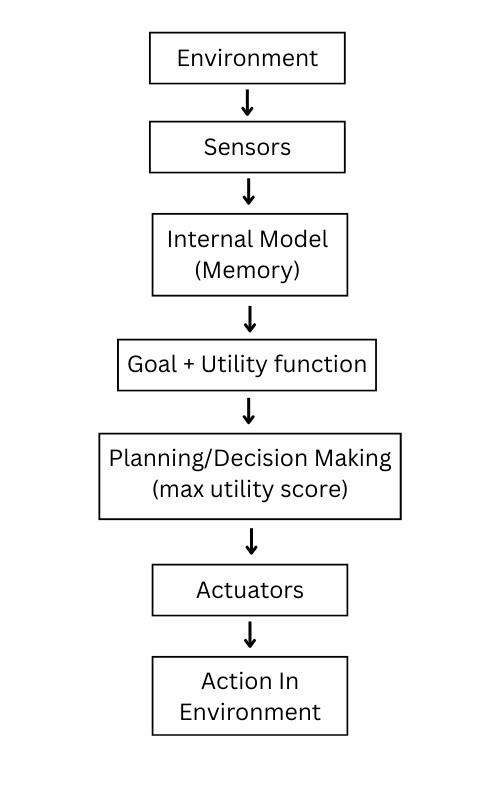
Use cases of utility based AI Agent
- Training bots in the game to improve its combat skills or particular task.
- Balancing delivery speed vs cost or optimizing inventory level vs demand satisfaction.
- Calculating mathematical expression or where reasoning are required to get alternative solutions.
5. Reinforce Learning Agent
Reinforcement learning agent is a type of agent that learn and improve it response over time. Unlike utility based agent, these agent aims to develop more accurate response through feedback mechanism.
Additionally, the mechanism have systematic architecture flow where it iterate response through learning element and critics evaluation.
For Example., An AI Agent playing multiple game but unfortunately keep loosing. After couple of days, it improve its combat skill and winning, thanks to feedback mechanism for iteration.
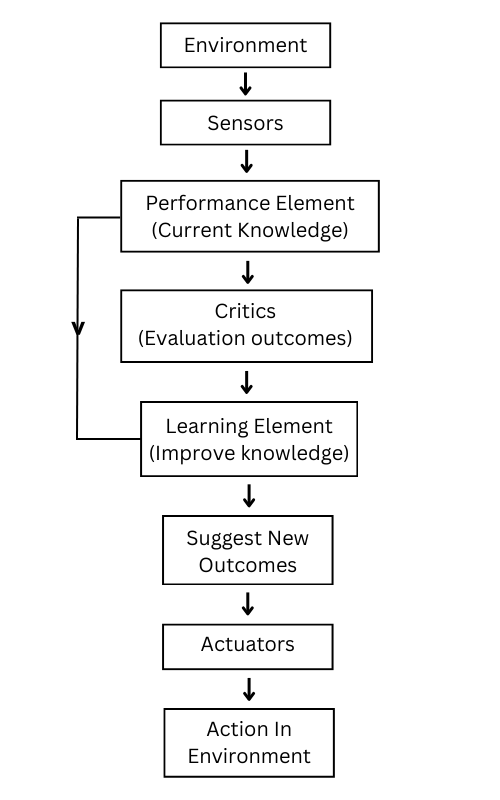
Use cases of reinforce learning AI Agent
- Movies recommendation on Netflix to improve future predictions.
- Drones uses mix of utility based as well as reinforce learning agent to improve aerial tasks.
- Improve patient health condition outcomes over time.
6. Multi-Agent System
A Multi-Agent System is a group of AI Models that are excel in their respective tasks. They are trained on huge corpus and fine-tuned for specific task like text generation, image generation, reasoning, coding and so on.
These agents can cooperate, compete, and work in a parallel toward specific goal. They can bring scalability, flexibility, and resilience to Artificial Intelligence.
For Example., Robotic Vehicle Coordination to guide best route to the destination by scraping traffic, weather, and road condition. Ecommerce recommendation where one agent analyzes user behavior, another recommends product, another monitors stock levels, and another handles pricing.
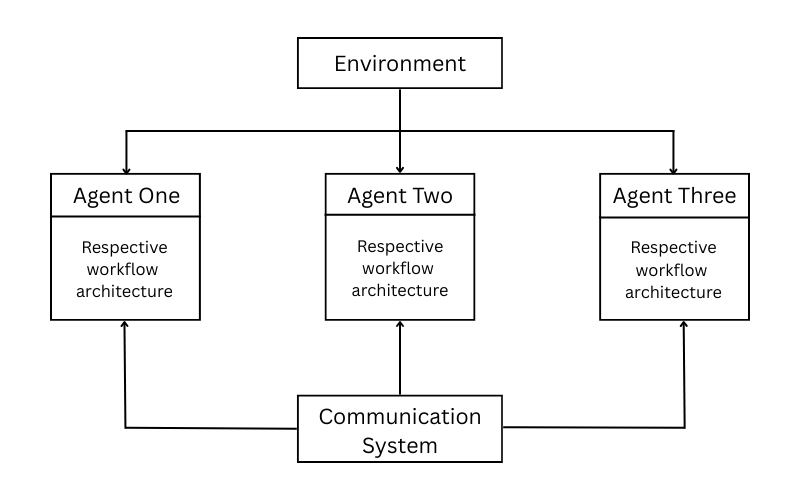
Use cases of multimodal AI Agent
- Virtual shopping assistant where customer input forms of data to get recommendation quickly.
- Diagnosis suggestions and treatment plans based on the sensitive data of patient.
- Personalized recommendations in app or voice guidance in-store kiosks used by Walmart.
Methods To Build AI Agents For Your Business
Low-code AI Agents and Full-code AI Agents are two methods for the development of AI Agents. While low-code platforms are gaining huge traction among individuals whereas full-code development consider as an advanced method to create custom, domain-specific AI Agents.
In this section, we’ll understand both methods in detail.
A. Low-Code AI Agents
No-code or low-code platform are versatile, fast, and convenient way to design, configure, and deploy AI Agents free of cost.
Basically, these platforms offer drag-and-drop interface to design Agentic workflow through pre-built Nodes, Connectors and so on.
Low-code tools like Bubble, n8n, Zapier AI Actions, Botpress, and Voiceflow are perfect for the development of AI Agents in variety of forms for an array of use cases. For instance., Botpress is a popular platform for creating text-based intelligence chatbot for eCommerce.
Popular No-code platform for AI Agent are Flowise AI and Zapier AI Actions for workflow automation from basic to complex task handling.
Additionally, accessing these platforms is easy because you don’t need technical or coding knowledge. The only limitation is platform’s limited flexibility and scalability.
B. Custom AI Agent
Custom AI Agent development demands in-depth knowledge of technology framework, programming language, and modern tech stacks. As these AI Agents are super intelligent and comes with full fledge of controllability.
Knowledge of Python fundamentals, LLM basics, and framework knowledge is absolute because of complex learning curve. For instance, LangChain for chaining LLM, memory, and tools. Autogen for multi-agent collaboration.
Complex autonomous agents, Financial trading agents balancing risk vs profit, Robotics agents with sensor, and Research assistants that browse, summarize, and draft reports are all examples of custom AI Agents.
While offer high flexibility, scalability, and integrity. It requires high programming knowledge, longer setup, and maintenance overhead.
Conclusion
AI Agents are at the forefront to tackle complex tasks to prevent human redundancy. And because they backed with an intelligent model, they can handle basic to complex tasks with speed and high accuracy.
An AI Agent is said to be both effective and efficient when it has well understanding of processing instructions, robust LLMs for Natural Language Processing, decent memory and tool usage to accomplish goals without obstacles or hallucination.
In the end, this guide might helped you learned about what AI Agent is, their components and types with methods available to build custom AI Agent solutions.
Do check our more guide on AI Agents below.
7 Types Of AI Agents & How To Pick The Right For Your Business
7 Agentic AI Trends In 2025 That No One Speak About
Agentic AI For Personalized Shopping Experiences In eCommerce
Frequently Asked Questions
What does an AI agent do?
An AI Agent understand the input, think before act, plan suitable procedure to accomplish the task autonomously using tools and large language models.
What is an example of AI Agent?
AI-powered home surveillance, autonomous vehicles, virtual assistance, devices like Alexa, and similar are examples of AI Agent models.
What are the six types of Agents In AI?
The six types of AI Agents are simple reflex AI Agent, model reflex AI Agent, goal-based Agent, utility based Agent, reinforce learning agent, and multimodal agent.
Are AI Agent frameworks complex?
No, they are not complex because AI Agent frameworks are platform that allow users to create seamless autonomous agents in form of chatbot with flexibility and simplicity. With drag and drop interface and pre-built LLMs, beginner can create and deploy AI Agents quickly.
Disclaimer: The information written on this article is for education purposes only. We do not own them or are not partnered to these websites. For more information, read our terms and conditions.
FYI: Explore more tips and tricks here. For more tech tips and quick solutions, follow our Facebook page, for AI-driven insights and guides, follow our LinkedIn page.
Bharat Kumar
Bharat is a content editor at The Next Tech for the past 3 years. He is studying Generative AI (GenAI) from Analytics Vidhya and share his learnings by writing on Generative Engines, Large Language Models, and Artificial Intelligence. In addition to his editorial work, Bharat is active on LinkedIn, where he shares bite-sized updates and achievements. Outside work, he’s known as a Silver‑rank Valorant player, reflecting his competitive edge and strategic mindset.
Related Posts
Artificial Intelligence
Agentic AI In Supply Chain Management: What It Enables That ...
By: Neeraj Gupta, Sun January 4, 2026
Supply chains today are more data-rich than ever. Foretelling models forecast..
Artificial Intelligence
Agentic AI Vs Chatbots 2026: Which One Can Actually Solve Co...
By: Neeraj Gupta, Sun December 28, 2025
Organizations have invested heavily in chatbots over the past decade, expecting..
Artificial Intelligence
How Odoo AI Integration Helps Teams Automate Complex Workflo...
By: Neeraj Gupta, Sun December 14, 2025
Even after implementing a powerful ERP like Odoo, many teams still collide with..
Artificial Intelligence
How AI Development Services Help Reduce Diagnostic Errors In...
By: Neeraj Gupta, Sat November 29, 2025
Diagnostic errors remain one of the most straining deficiencies in healthcare..
Artificial Intelligence
What Users Really Want To Know: Business Central Vs Dynamics...
By: Neeraj Gupta, Sat November 22, 2025
Most users comparing Business Central vs Dynamics 365 CRM aren’t disoriented..
Artificial Intelligence
Top AI Data Visualization Frameworks That Are Fueling Produc...
By: Neeraj Gupta, Sun November 16, 2025
In any research lab or startup, one global problem persists: you have tons of..
Copyright © 2018 – The Next Tech. All Rights Reserved.







