Unlike Google, which indexes and crawls webpages, LLMs like GPT-4.1 (ChatGPT intelligent model) follow a different approach to cite new content, and it’s useful for developers, researchers, data scientists, and end users to understand these pipelines.
Their responses are generated from patterns and information they absorbed during training on a large, but static training corpus with a fixed knowledge cutoff of June 2024. If your article was published after that date, it won’t appear in parametric citations.
But have you ever wondered how LLMs cite new content or display your website link for a particular query? Basically, when they do provide citations, they use one of two methods:
One, Static Training Data
During its training, they absorbed patterns from a huge corpus of publicly available web pages, forum posts, news articles, research papers and blogs. If your article was indexed and widely referenced online before that cut-off, it may have “learned” its key facts, structure and even phrasing.
For example; When a user query aligns closely with the topic you covered, the model can surface what it “knows” about that content, sometimes even reconstructing a citation that looks like a URL or article title.
Two, Browser Enabled Mode
When live retrieval is enabled via a REST API call, the model performs a query using retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). It encodes your question in embedding space, searches a vector database (e.g., FAISS or Annoy) for the closest document chunks, then includes and cites them.
For example; If your content ranks highly for the keywords in the user’s question, GPT-4 large language model retrieve it live via the browser tool, verified the relevant passage, and then formatted the citation.
Table of Contents
How Do LLMs Retrieve Information To Cite?
There are two major techniques utilized by LLMs to retrieve information or knowledge when a model answers your question.
1. Parametric Memory via the Model’s Weights
During pre-training, the model learns to associate words, facts, and patterns by adjusting billions of parameters. At inference, the model uses its stored parameters to retrieve patterns directly from training. This process is instantaneous but limited to the training data and knowledge cutoff.
2. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
When the web search feature is enabled, the model issues a crawling and indexing query, populates an embedding index, then performs vector search. Retrieved passages are added to the prompt after tokenization, creating tokens that respect the model’s context window (e.g., 32k tokens) and then used for citation generation.
- When you asked questions to ChatGPT, your questions encoded into document embedding space.
- Source documents (web pages, PDFs, your blog posts, etc.) are broken into chunks and encoded into high-dimensional embedding vectors.
- GPT-4 utilizes FAISS or Annoy vector search to find the chunks whose embeddings are closest to your query’s embedding.
- At final, those retrieved context are carefully ponder to the model’s input, so the generator can quote or summarize them, then cite them explicitly.
FAISS (Facebook AI Similarity Search) and Annoy (Approximate Nearest Neighbors Oh Yeah) are libraries used for fast similarity search in embedding space.
Now the real question arises here is how long does it take ChatGPT to cite new content. Let’s understand in the next section.
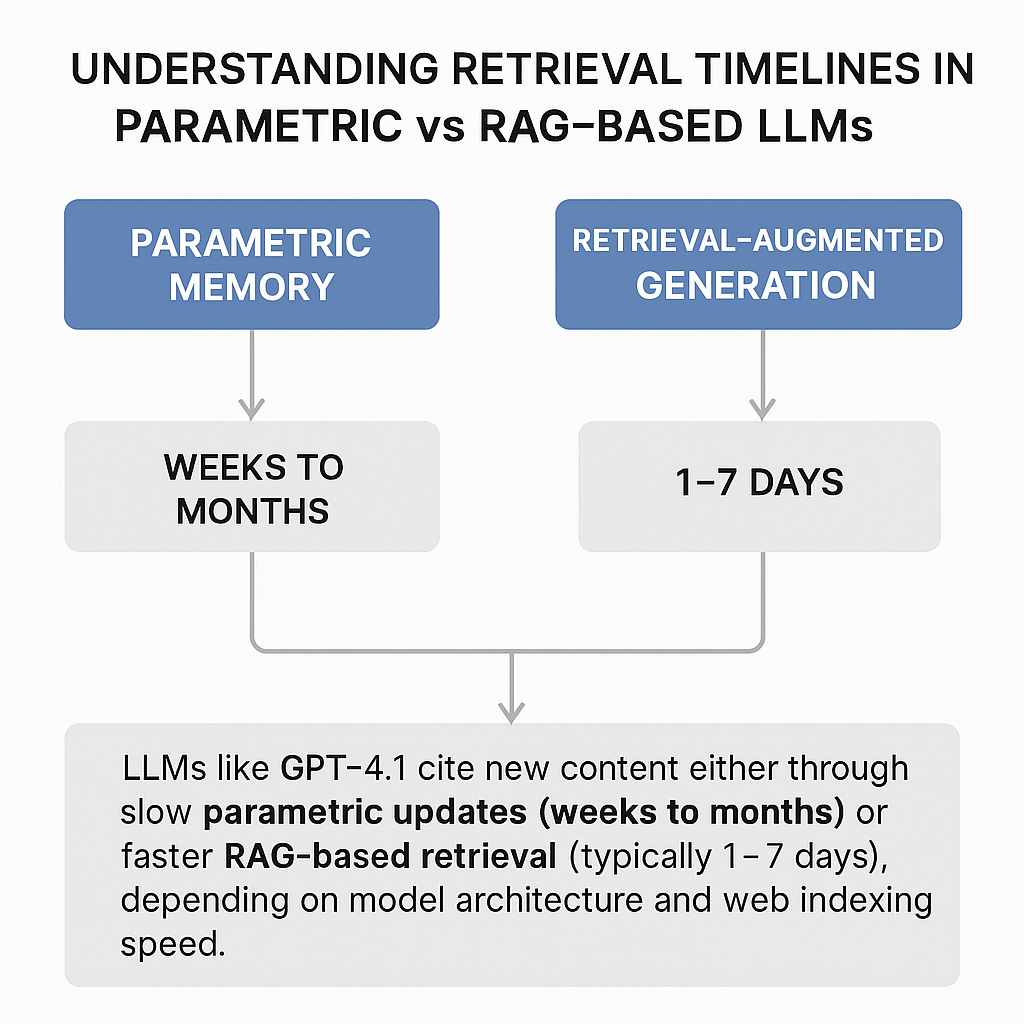
Understanding Retrieval Timelines In Parametric vs RAG-based LLMs
1. Parametric Memory (Model Weights)
GPT-4.1 series including GPT-4.1 Mini, and GPT-4.1 Nano models were released in the OpenAI API in April 2025 and are now being integrated into ChatGPT which are excel in coding and long-context understanding, with a refreshed knowledge cutoff of June 2024.
I have tested few queries with this model, and it fails to provide latest information for some queries while it generate logical reasoning answers on other queries.
For example; I asked “What is GLM 4.5 and GLM 4.5 Air?” and it answers the question regardless of its knowledge cut off to June 2024. That generated answer was based on logical reasoning by pertaining the organization past information.
So, the approximate duration would be anywhere from weeks to a few months to retrieve information or unless new model released with updated knowledge.
2. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
The GPT-4.1 can also learn about your new content through RAG technique by implying document chunking and embedding. This happen using the public search engine (crawling and indexing) latency approach which would take anywhere from hours to several weeks, most often 1–7 days, depending on site authority, crawl budget, and sitemap submission.
A high authority website content would typically get cited by ChatGPT earlier than low authority webpages. This take us back to SEO fundamentals where aim for a high-quality backlinks is important.
For example, I tested two websites; one with high domain authority and another with low domain authority.
- Geekflare (DA: 61 and PA:57) with queried searched for “10 best face swap ai tools”
- Pykaso (DA: 19 and PA: 29) with queried searched for “how to face swap with AI”
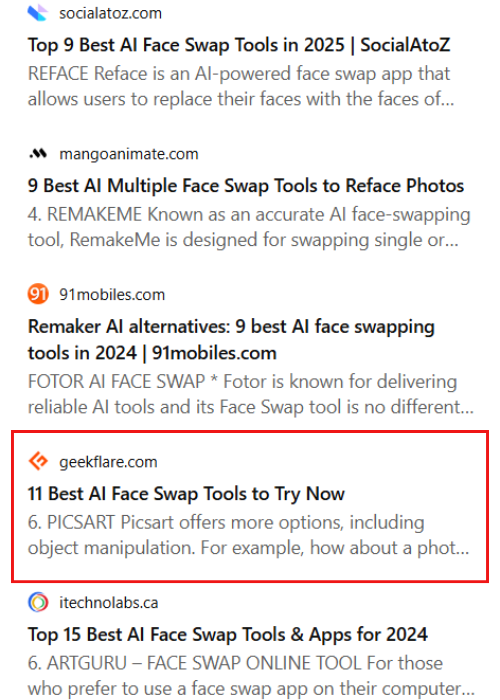
As a result, Geekflare blog content appeared whereas Pykaso blog content fails to appear in the ChatGPT. Ironically, LLMs prioritise content that are authoritative, well-written, and AI-structured friendly.
10 Hacks For AI-Friendly Content Generation
Writing for user should be your aim rather writing for ranking. AI Engines prioritise content that are well structured, direct and short answer without bluffing other context.
#1. Create High-Quality, Authoritative Content
Write articles that put your readers first. Answer their real questions using trustworthy sources and fresh ideas. Make sure your writing is original, detailed, and human-written so both AI tools and people see you as an expert.
#2. Format Your Content As Per User Intent
Think about what your readers want: a step-by-step guide, a quick list, a comparison, or FAQs. Use the right headings, bullet points, and layouts so AI can easily understand and show your page to the right audience.
#3. Explain In Plain Text As Much As Possible
Give straightforward answers in simple paragraphs. Avoid fancy UI or hidden text because AI needs plain text to pick out the main points quickly. Keep your tone friendly and to the point.
#4. Create Subheadings Based On Q&A Intent
Turn your subheadings into questions like “What is X?” or “How to do Y?” This tells AI exactly what question you’re answering and helps your content show up in quick-answer boxes.
#5. Solid On-Page Optimization
Write clear titles, useful meta descriptions, proper heading levels (H1, H2, H3), internal links, alt text for images, and make sure your page works well on mobile. These steps help AI read and rank your page better.
#6. Use Of Schema Markup
Add simple code snippets to your page like Article, FAQ, or HowTo tags so AI and voice assistants know exactly what your content is about and can feature it in rich results.
#7. Mention Number Stats & Quotes
Include up-to-date numbers and expert quotes in your posts. AI search engine love fact-based content, and solid statistics and chances of being featured.
#8. Be Present On LLM Training Data
Share your expertise on public platforms like Reddit, Wikidata, reputable news sites, or GitHub. AI models often learn from these sources, so being there increases your visibility in AI-driven search results.
#9. Get Mention By Other Authoritative Brands
Aim for backlinks or mentions from big-name sites. These endorsements act like votes of confidence, helping AI recognize your site as a trusted resource.
#10. Regularly Update Your Content
Keep your articles fresh by adding new stats, examples, or insights over time. AI favors content that stays current.
Key Takeaway
Large language models like GPT-4.1 retrieve content either through built-in parametric memory (static training data) or live retrieval using techniques like RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation).
- ChatGPT’s LLM may cite your webpages only when its indexed, authoritative article, and well-structured.
- Use the aforementioned hacks to generate high-quality content and chance to cite your new content.
In the end, it’s all about producing helpful, people-first content while optimizing for Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) to boost brand visibility and traffic.
Author’s Recommendation:
ChatGPT Plus: Price, Availability, How To Upgrade
17 Connectors In ChatGPT Available On Demand
60+ ChatGPT Prompts You Should Know
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does GPT-4 take to cite new content?
If using web browsing (RAG), it can cite content in 1–7 days after it is indexed by search engines. Otherwise, it requires a new model update, which may take months.
Does GPT-4.1 access the live web?
Not by default. It only accesses the live web when browsing or retrieval tools are enabled.
Can GPT-4.1 cite my blog or website?
Yes, if your content is indexed, ranks well, and is relevant to the user query, it can be cited and appear in the sources along with other webpages.
What to publish so LLMs actually cite you?
Draft and publish content related to structured best of lists, first-person product reviews, FAQ-style content, and so on.
Where to publish so LLM cite your content quickly?
Medium, Substack, and Linkedin Articles are great platforms to publish and increased chance of LLM seeding your content.
Why isn’t my article cited by AI Engines?
Either your content is not indexed yet, it ranks low or not well structured, or poorly written article that not compiled with EEAT principle.
Disclaimer: The information written on this article is for education purposes only. We do not own them or are not partnered to these websites. For more information, read our terms and conditions.
FYI: Explore more tips and tricks here. For more tech tips and quick solutions, follow our Facebook page, for AI-driven insights and guides, follow our LinkedIn page.
Top 10 News
-
01
Top 10 Deep Learning Multimodal Models & Their Uses
Tuesday August 12, 2025
-
02
10 Google AI Mode Facts That Every SEOs Should Know (And Wha...
Friday July 4, 2025
-
03
Top 10 visionOS 26 Features & Announcement (With Video)
Thursday June 12, 2025
-
04
Top 10 Veo 3 AI Video Generators in 2025 (Compared & Te...
Tuesday June 10, 2025
-
05
Top 10 AI GPUs That Can Increase Work Productivity By 30% (W...
Wednesday May 28, 2025
-
06
[10 BEST] AI Influencer Generator Apps Trending Right Now
Monday March 17, 2025
-
07
The 10 Best Companies Providing Electric Fencing For Busines...
Tuesday March 11, 2025
-
08
Top 10 Social Security Fairness Act Benefits In 2025
Wednesday March 5, 2025
-
09
Top 10 AI Infrastructure Companies In The World
Tuesday February 11, 2025
-
10
What Are Top 10 Blood Thinners To Minimize Heart Disease?
Wednesday January 22, 2025







