In the context of entity seo, Google has strengthen its retrieval information using Natural Language Processing (NLP) to generate accurate, personalized, and rightful information.
Previously, the Knowledge Graph Panel, Featured Snippets, and People Also Ask (PAA) were key mediums for entity optimization for brands and individuals. In fact, Google’s Knowledge Graph contains over 500 billion facts about 5 billion entities.
Since then Google MUM, SGE, and LLM have revolutionized entity retrieval and changed the arc of Search Engine Optimization.
Today’s competition is about fighting for visibility on AI Overviews which is indeed a fact that you must be produce authoritative and entity-optimized content.
I have shared an important details with SEO professionals, bloggers, and content strategists on how to find right entities and optimize in content.
Table of Contents
What Is Entity SEO?
Entity SEO emphasizes the meaning behind words by identifying people, places, organizations, and concepts that search engines can understand and connect in a Knowledge Graph.
Entities in SEO are different from keywords as they are not address words used in query search, but entities are the singular, distinct description of things or concept used to identify search query accurately.
Example:
Take the word “Apple”—it could mean the tech company or the fruit. Google identifies each as a distinct entity based on context and background knowledge.
- When you search “Apple” it always show you result about tech giant Apple Inc.
- When you search “Apple fruit” it show result about edible fruit of an apple tree.
Search engines understand about entities by exploring the words inside Knowledge Graph, Wikidata, and Wikipedia to form a structured understanding of entities and how they relate to one another.
Difference Between keyword vs Entities
An important difference is that Keyword help with what users typing and Entities help what users actually mean.
Crunching the above context. Keyword are words or phrases used in searches. They can be questions, sentences, or a word. For example, “best laptop” or “best phone in 2025”
Entity, on the other hand, a word that is singular, unique, well-defined and distinguishable often categories into people, places, things, and objects. For example, “Apple Inc.” (company), “iPhone 15” (product), “Tim Cook” (person), etc. Entities are the digital representation of the “things” people search for. An entity guides search engines to understand clear and distinguish words based on their emotion.
Keywords and entities have separate importance in content. Keywords still matter because they connect your content to queries. Entities are important to help search engine understand how various words are connected and defined, focuses on semantic understanding.
How To Find Right Entities For Your Content
Manual entity seo scraping are time taking. Therefore, I use tool-based method because convenient, less-learning curve, and efficient.
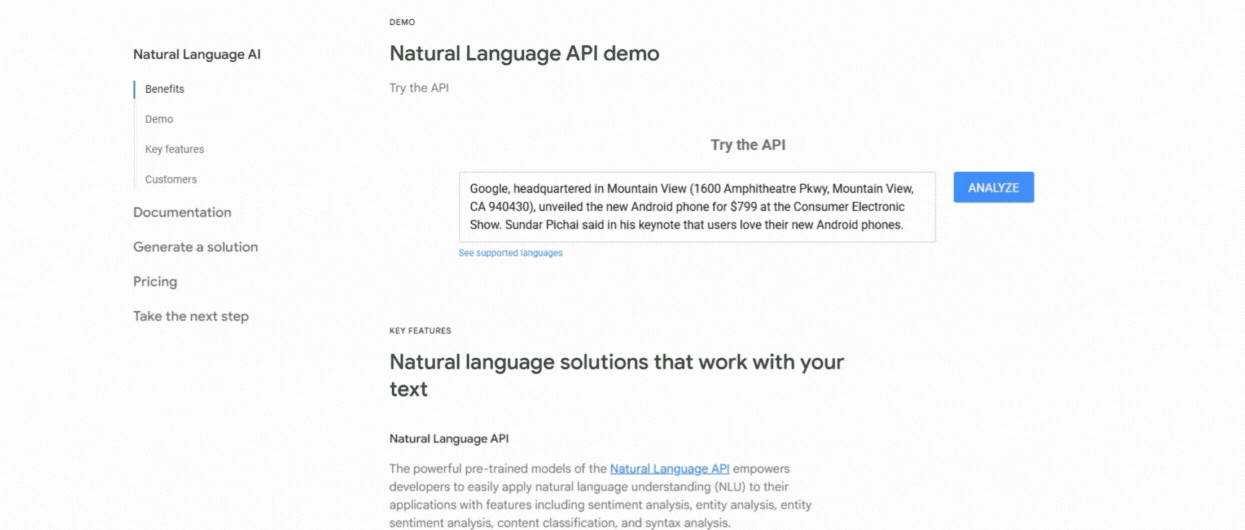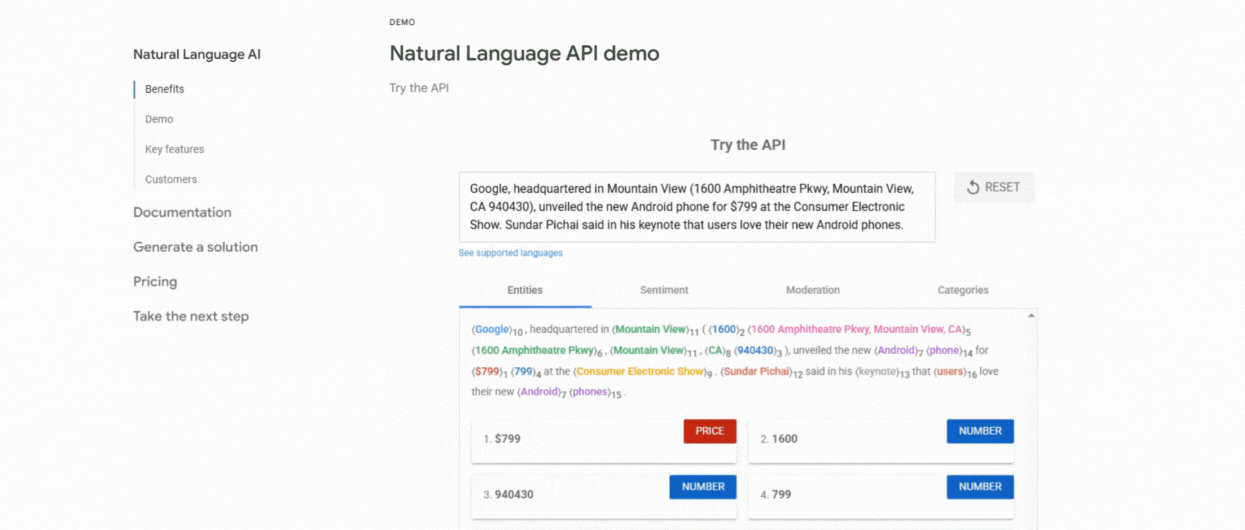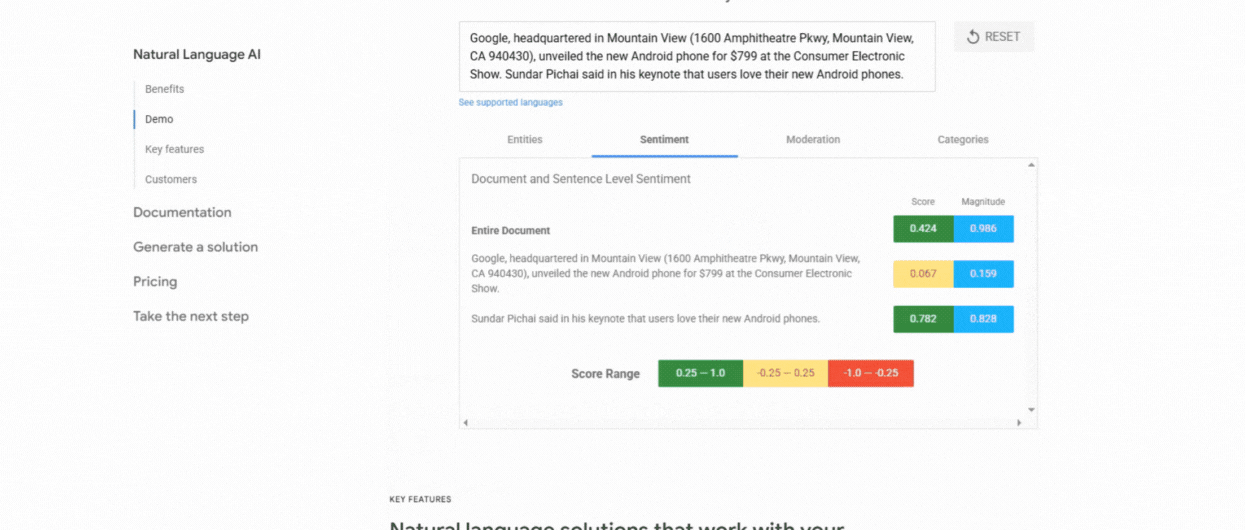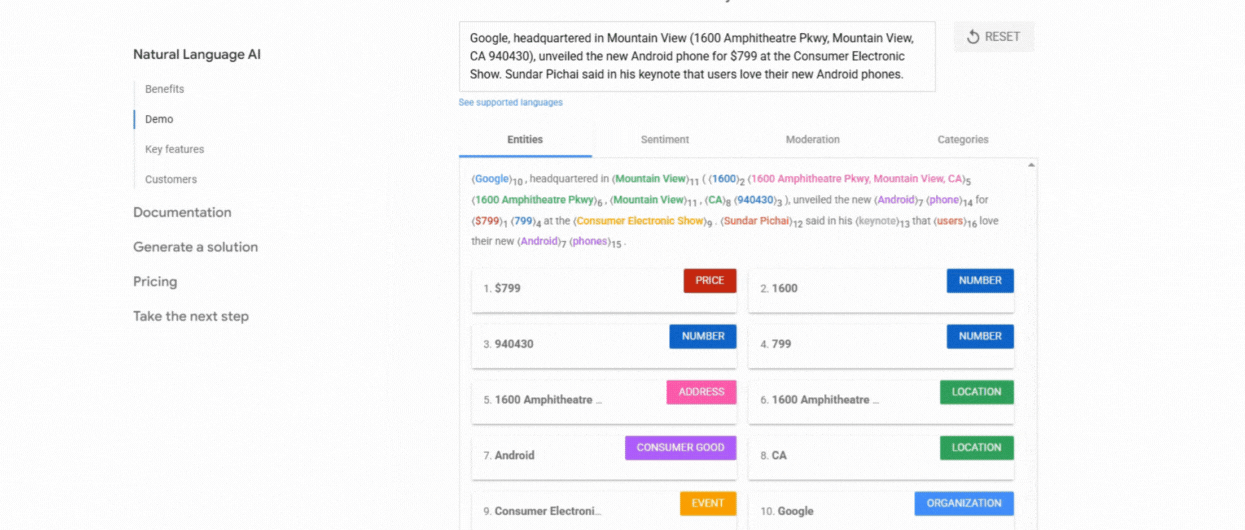
1. Use Google NLP API
This tool analyzes your content and highlights the entities Google recognizes along with their importance, types (Person or Organization), and links to Knowledge Graph entries. It is great for understanding how Google itself interprets your content semantically.
2. ChatGPT
In a conversational style, you can prompt GPT-4 to extract entities from a paragraph, identify their relationships, or even generate entity maps. It is great for quick, structured analysis of any text using natural language. You can even ask to format entities in specific style. For example, [Entity 1]–(relation)–>[Entity 2] and you can dig deeper to understand characteristic or properties of each entities to understand their relationship more better.
Also read: [10 Best] Blog To Video AI Free (Without Watermark)How To Optimize Entities In Content
Entities optimization can be done through entity mapping, refers to a series of procedure consist entity identification, entity attribution, and discover relationship.
Below I have shared a tested example of entity mapping using ChatGPT based on Topic idea “How to control temperature in a charcoal smokes?”
1. Lists the main nouns (people, places, things and concept) that are central to the topic.
A. People
- Pitmaster
- Griller
- Barbecue enthusiast
- Chef
- Beginner
B. Places
- Grill area
- Firebox
- Vents (Top vent, bottom vent)
- Cooking chamber
- Outdoors / Backyard
C. Things
- Charcoal
- Smoker
- Grill
- Thermometer
- Chimney starter
- Water pan
- Wood chips / Wood chunks
- Fire grate
- Air vents / Dampers
- Lighter fluid (optional)
- Heat deflector
- Ash catcher
- Fuel (briquettes, lump charcoal)
D. Concepts
- Temperature control
- Airflow
- Heat zones (direct/indirect heat)
- Smoking time
- Fuel management
- Oxygen flow
- Heat retention
- Vent adjustment
- Low and slow cooking
- Target temperature range
- Temperature spikes/drops
2. For each entity, lists key attributes (characteristics or properties).
A. PEOPLE
1. Pitmaster / Griller / Barbecue Enthusiast
- Experience level (beginner, intermediate, expert)
- Cooking style preference (low & slow, hot & fast)
- Knowledge of airflow and heat control
- Patience and attention to detail
- Tools used (thermometer, gloves, charcoal type)
B. PLACES
2. Grill Area / Outdoors
- Wind conditions
- Ambient temperature
- Shelter or exposure to elements
- Safety distance from flammable structures
3. Firebox / Cooking Chamber
- Heat retention capability
- Size and shape
- Material (steel, ceramic, etc.)
- Distance from fuel to food
- Air circulation pattern
4. Vents (Top / Bottom)
- Adjustability (open, half-open, closed)
- Size and number of vents
- Placement (top for exhaust, bottom for intake)
- Influence on airflow and oxygen supply
C. THINGS
5. Charcoal
- Type (briquettes vs lump)
- Burn time
- Heat Intensity
- Ash production
- Ease of ignition
6. Smoker
- Type (offset, vertical, barrel, kamado)
- Insulation quality
- Lid seal tightness
- Internal volume
- Vent and grate configuration
7. Thermometer
- Accuracy
- Type (built-in, digital, probe)
- Placement (grate-level, dome, meat)
- Response time
8. Chimney Starter
- Size (capacity for charcoal)
- Heating speed
- Ease of lighting
- Ventilation efficiency
9. Water Pan
- Size and depth
- Water holding capacity
- Humidity regulation
- Heat absorption
- Placement in smoker
10. Wood Chips / Chunks
- Type of wood (hickory, apple, mesquite)
- Smoke intensity
- Burn rate
- Flavor profile contribution
11. Air Vents / Dampers
- Material (metal, plastic)
- Control mechanism (manual or adjustable dial)
- Resistance to heat warping
- Responsiveness to changes
12. Fuel (Briquettes, Lump Charcoal)
- Consistency
- Ash residue
- Flavor impact
- Temperature control capability
D. CONCEPTS
13. Temperature Control
- Precision
- Responsiveness to changes
- Stability over time
- Adjustment frequency
14. Airflow
- Direction (intake to exhaust)
- Volume of air
- Impact on combustion
- Relation to vent position
15. Heat Zones (Direct / Indirect Heat)
- Placement of coals
- Cooking method (searing vs smoking)
- Temperature difference between zones
- Zone separation technique
16. Fuel Management
- Replenishment frequency
- Charcoal stacking method (snake, minion, pyramid)
- Pre-lighting method
- Burn control
17. Low and Slow Cooking
- Ideal temperature range (225–250°F / 107–121°C)
- Cooking duration
- Smoke penetration
- Moisture retention
18. Temperature Spikes / Drops
- Causes (wind, lid opening, fuel overload)
- Recovery methods
- Prevention tips
- Monitoring tools
3. Describe how entities relates to each other. Create a visual map showing how the entities connect. Provide an output in the following fashion “[Entity 1]–> (relation)–> [Entity 2]”
A. Fuel & Heat Source Relationships
[Charcoal] –> (burns to generate) –> [Heat], [Heat] –> (increases) –> [Cooking Chamber Temperature], [Wood Chips / Chunks] –> (produce) –> [Smoke], [Charcoal] –> (placed in) –> [Firebox], [Firebox] –> (sits inside) –> [Smoker]B. Airflow & Ventilation
[Air Vents] –> (control) –> [Airflow], [Airflow] –> (controls combustion in) –> [Charcoal], [Airflow] –> (affects) –> [Heat Production], [Bottom Vents] –> (intake) –> [Oxygen], [Top Vents] –> (exhaust) –> [Smoke & Heat]C. Temperature Control
[Airflow] –> (controls) –> [Temperature], [Water Pan] –> (regulates) –> [Humidity], [Water Pan] –> (stabilizes) –> [Heat Fluctuations], [Thermometer] –> (measures) –> [Cooking Chamber Temperature], [Smoker Type] –> (influences) –> [Heat Retention], [Pitmaster] –> (adjusts) –> [Vents], [Pitmaster] –> (manages) –> [Fuel Supply]D. Cooking Process
[Cooking Chamber Temperature] –> (determines) –> [Cooking Time], [Heat Zones] –> (created by) –> [Charcoal Placement], [Meat] –> (placed in) –> [Cooking Chamber], [Pitmaster] –> (uses) –> [Thermometer], [Low & Slow Cooking] –> (requires) –> [Stable Temperature], [Stable Temperature] –> (achieved by) –> [Fuel Management], [Charcoal Type] –> (affects) –> [Burn Time and Heat Output]E. Environmental Factors
[Wind] –> (affects) –> [Airflow], [Ambient Temperature] –> (influences) –> [Heat Loss or Retention], [Outdoor Environment] –> (impacts) –> [Smoker Efficiency]F. Grill Configuration
[Smoker] –> (contains) –> [Firebox], [Cooking Chamber], [Air Vents], [Firebox] –> (holds) –> [Charcoal], [Wood Chunks], [Cooking Chamber] –> (holds) –> [Water Pan], [Meat], [Thermometer]After collecting entities, use these while drafting your content. Adding most of these entities make your draft reliable, accurate, and strong for search engines.
- Add contextual links to Wikipedia, Wikidata, or authority sites.
- Update headings, subheadings, and anchor texts with primary and secondary entities.
- Use JSON-LD schemas to define the entities (e.g., Person, Organization, Product).
Benefits Of Entities Optimization
One of the significant benefits of entity seo is that it goes beyond keywords, making your content with how search engines and AI understand the world.
1. Stronger Topical Authority
When you consistently cover related entities in-depth, search engines recognize your site as a trusted source in your niche. This strengthens your topical relevance and improves rankings across semantically related queries.
2. Better AI Comprehension
Search engines (like Google AI Overviews) and language models (GPT-4o) use entity-based understanding to interpret content. Well-optimized entities help these systems extract accurate answers.
3. Higher Chances of Featured Snippets
Google pulls structured information from entity-rich content to display; featured snippets, knowledge panel, people also ask, and carousels (FAQs).
Final Thought
Optimizing content based on entities parameters is a great way to show authority, expertise, and trust to search engine and get higher ranking than your competitors. A few more consideration while optimizing for entity SEO.
- List your business or brand on authoritative platforms.
- Get customer reviews to increase brand of mouth.
- Gain relevant, authoritative backlink from niche websites.
Though, entities optimization is not an easy task, it takes time, knowledge, and hard work. As I am learning more on Generative Engine Optimization and GenAI – I’ll keep updating this post for up-to-date information.
In the end, I do recommend seo professionals, seo writers, and content strategist to use entity seo in their content. Also, I would love to hear your thoughts. Thanks for reading 🙂
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is entity optimization important for SEO?
It helps search engines and AI tools better understand your content, improves topical authority, and increases your chances of ranking in featured snippets, Knowledge Panels, and Google SGE results.
Does Google use entities in its ranking algorithm?
Yes. Since the introduction of the Knowledge Graph and Hummingbird update, Google increasingly focuses on semantic search and entity understanding.
Is keyword research still needed if I optimize for entities?
Yes, keyword optimization still important to address queries and entities to help search engines understand relationship across queries accurately.
Can I add entity schema to my blog?
You can use Schema markup (like Person, Organization, Product, or Article) to help search engines understand the entities mentioned on your page.
Disclaimer: The information written on this article is for education purposes only. We do not own them or are not partnered to these websites. For more information, read our terms and conditions.
FYI: Explore more tips and tricks here. For more tech tips and quick solutions, follow our Facebook page, for AI-driven insights and guides, follow our LinkedIn page.
Update Timelines:
August 11, 2025 – Added important suggestions in the conclusion.
Top 10 News
-
01
Top 10 Deep Learning Multimodal Models & Their Uses
Tuesday August 12, 2025
-
02
10 Google AI Mode Facts That Every SEOs Should Know (And Wha...
Friday July 4, 2025
-
03
Top 10 visionOS 26 Features & Announcement (With Video)
Thursday June 12, 2025
-
04
Top 10 Veo 3 AI Video Generators in 2025 (Compared & Te...
Tuesday June 10, 2025
-
05
Top 10 AI GPUs That Can Increase Work Productivity By 30% (W...
Wednesday May 28, 2025
-
06
[10 BEST] AI Influencer Generator Apps Trending Right Now
Monday March 17, 2025
-
07
The 10 Best Companies Providing Electric Fencing For Busines...
Tuesday March 11, 2025
-
08
Top 10 Social Security Fairness Act Benefits In 2025
Wednesday March 5, 2025
-
09
Top 10 AI Infrastructure Companies In The World
Tuesday February 11, 2025
-
10
What Are Top 10 Blood Thinners To Minimize Heart Disease?
Wednesday January 22, 2025